AEROSPACE
A major part of ACETEC’s Aerospace focus is on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) which is expected to surpass manned aircraft numbers in the next 5 years. The purpose of a UAS is to deliver or collect data usually in a dull, dirty or dangerous environment. The effectiveness of the payload itself is the most important element of the entire UAS system, as this determines the ROI of the effort. The vehicle itself does not deliver the message or the data: it merely gets the payload to the best location.
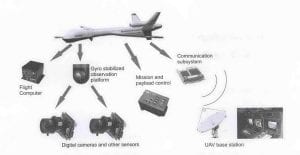
UAS can be encompassed into these four succinct elements and sub-elements:
- Payload control system: sets of sensors such as for thermal, video, and infrared signals that gather intelligence where its processed on board or transmitted to a ground station for further analysis. Critical to the mission, these functions are also aboard:
- Payload
- Electro-optical Sensing Systems and Scanners
- Infra-Red Systems
- Radars
- Dispensable loads (Munitions, flares, sondes, etc)
- Environmental sensors
- Ground control system or station: the use of laptop computers, communication equipment, and other modular electronics that users can transport rather easily.
- An avionics flight display
- Navigation Systems
- System Health Monitoring and Prognostics Display
- Graphical Images and Position Mapping
- Secure Communications Systems
- Flight control computer or system: ensures the UAS follows the pre-programmed or ground control station-updated mission flight path in the most economical way avoiding obstacles and other air users. One or more can be carried on a UAS at any one time. It should be noted that munitions will never legally be permitted to be carried on a UAV operating in European and American civil airspace.
- The vehicle or platform itself: includes the airframe and propulsion System
- The precision navigation system: telemetry and datalink communications through one or multiple antennas
- Sense & Avoidance System: the means to deliver the payload to its optimal position. UAS operate at all altitudes and the propulsion system has to be tailored to the mission.
- The diagram below depicts an entire UAS network:
8. The Ground Control Station (GCS) in tomorrow’s UAS environment will be part of an integral part of managed airspace. It will house the UAS pilot and the UAS commander and will appear to the outside world as if both people are actually on board the air vehicle.
To achieve all this, the GCS must have secure communications with both the air vehicle and the international, national, regional and local air traffic management infrastructure.